Dreaming of sustainable gardening but don’t have enough space, land, or the right climate? Hydroponics could be the perfect solution for you.
Today, I’ll dive into hydroponics for beginners, breaking down how these gardening systems work, the plants you can grow, and the different types. I’ll also share some tips on how you can keep your hydroponic garden healthy.
Understanding how hydroponics works will help you choose the right plants to grow and decide if this gardening method fits your preferences and goals.
5 Key Takeaways on Hydroponics
- Hydroponics is a method of growing plants without soil that has been around for centuries. It uses nutrient solutions in water to grow plants instead of soil.
- There are various hydroponic systems like deep water culture, drip irrigation, and aeroponics, each offering unique benefits.
- Hydroponics isn’t just a hobby. It’s also a solution to global food challenges, offering sustainable farming practices for the future.
- Gardeners have precise control over light, temperature, humidity, and pH levels with hydroponics. The process optimizes plant growth regardless of external conditions.
- While not all plants are suited for hydroponics, leafy greens, herbs, and smaller fruits thrive in this system. This type of garden offers fresh produce year-round with minimal space requirements.
Understanding Hydroponics and Its History

Hydroponics may feel like a cutting-edge gardening technology that started in the last decade, but it’s been around for almost 400 years. It’s a method of growing plants using nutrient-filled water, sometimes using a hydroponic medium such as peat moss, in place of soil. Various types of hydroponic gardening include deep water culture, drip irrigation, and aeroponics.
Hydroponics has a long history that dates back to 1627 when Sir Francis Bacon first wrote about it. John Woodward’s experiments with spearmint followed in 1699. By 1842, it gained popularity in Europe under the name “aquaculture.” Germany, France, Spain, and Italy welcomed this new agricultural technology, conducting their own experiments.
The term “hydroponics” was coined by William Frederick Gericke in the 1930s. Modern hydroponics is revolutionizing agriculture despite its ancient origins. Today, hydroponics isn’t just a hobby. It’s also a solution to global food issues.
Regardless of what hydroponics is called, it refers to one of the more popular indoor gardening solutions acting as a substitute for soil.
How Does Hydroponics Work?
Unlike traditional soil-based systems, hydroponics grows plants using only water and nutrients. Pumps, pipes, and equipment deliver these essentials directly to the plant roots. This promotes healthy plant growth and requires less space.
Seeds aren’t buried in the soil. They’re placed on a grow tray in a water and nutrient-filled container instead.
The ratios used in hydroponics are carefully adjusted for each plant type. Hydroponic culture uses 90% less water than traditional gardening because water and nutrients go straight to the roots.
Gardeners can control the following in hydroponics:
- Light
- Temperature
- Humidity
- pH levels
The process does not rely on sunlight or rain. Conditions are tailored for rapid growth instead. This flexibility means you can grow crops like citrus fruits in unexpected places with higher crop yields than traditional methods.
Progress is closely monitored throughout the growth cycle, allowing for precise harvest timing and continual improvement of hydroponic food production.
You’ll learn to prepare the space needed, manage water quality, adjust artificial light, and more for a thriving hydroponic garden.
- Read more about Grow Light for Hydroponics
What Plants Can You Grow With Hydroponics?

In theory, anything that thrives in soil can also flourish in a hydroponic system. However, imagining rows of corn sprouting from your kitchen counter might not be appealing!
Certain plants, like lettuces, strawberries, bell peppers, and cherry tomatoes thrive in hydroponic setups. Leafy greens and herbs, in particular, thrive indoors, offering fresh salad fixings year-round with minimal effort.
- Learn more about the Best Hydroponic Plants to Grow
However, root vegetables and larger plants aren’t as compatible with small-scale hydroponics.
Crops like corn and vines, such as grapes, aren’t well-suited for hydroponics as well due to their root systems and size. While artificial lighting, like LEDs, has improved, some plants, like sunflowers and berries, still prefer natural sunlight.
- Get more information on the Best Seeds for Hydroponics
Understanding the light needs of each plant is crucial for successful hydroponic gardening. It’s not just about brightness but also about timing and positioning to ensure optimal growth.
Keeping Your Plants Healthy With Hydroponic Nutrients

Hydroponic nutrients are like the life force of your hydroponic setup. Water is important, but it’s the nutrients that truly get the job done.
Plants have to search for their food in the soil, but we serve it up to them in hydroponics. Getting the right balance is key. Too little, and they go hungry but too much, and they’re overwhelmed.
I’ve carefully crafted my hydroponic solutions over time, ensuring that each plant gets exactly what it needs. It’s a journey, but every step is worth it.
Roots still need support even though there’s no soil. I’ve found materials like vermiculite, clay pebbles, and coconut fiber to be perfect. They keep things stable while holding onto moisture but still spread nutrients effectively.
Managing Water Quality for Hydroponics
Water quality is crucial in hydroponics. Many gardeners overlook this and regret it later. This factor can either make or break your system.
It is important to note that your plants live in this water environment so any contaminants go directly to them. Therefore, regularly testing and adjusting the water, nutrients, and pH levels in your hydroponic garden is very important.
Use clean, filtered water with a pH level of around 6–6.5. This helps your plants get the perfect balance of nutrients.
It’s not just about feeding your plants. It is also about creating a healthy space for them. Treat your water carefully, and you’ll see your plants thrive.
Also, make sure your plant roots get enough oxygen. Leave some space between the plant base and the water reservoir, or oxygenate the water. Think of it as giving your plants a breather so they don’t suffocate.
What Are the Different Hydroponic Systems?
There are several types of hydroponic systems, each with its benefits. Understanding these systems can help you choose the best one for your gardening needs.
Here are some of the most popular hydroponic systems and how they work.
1. Wick System – Best for Beginners
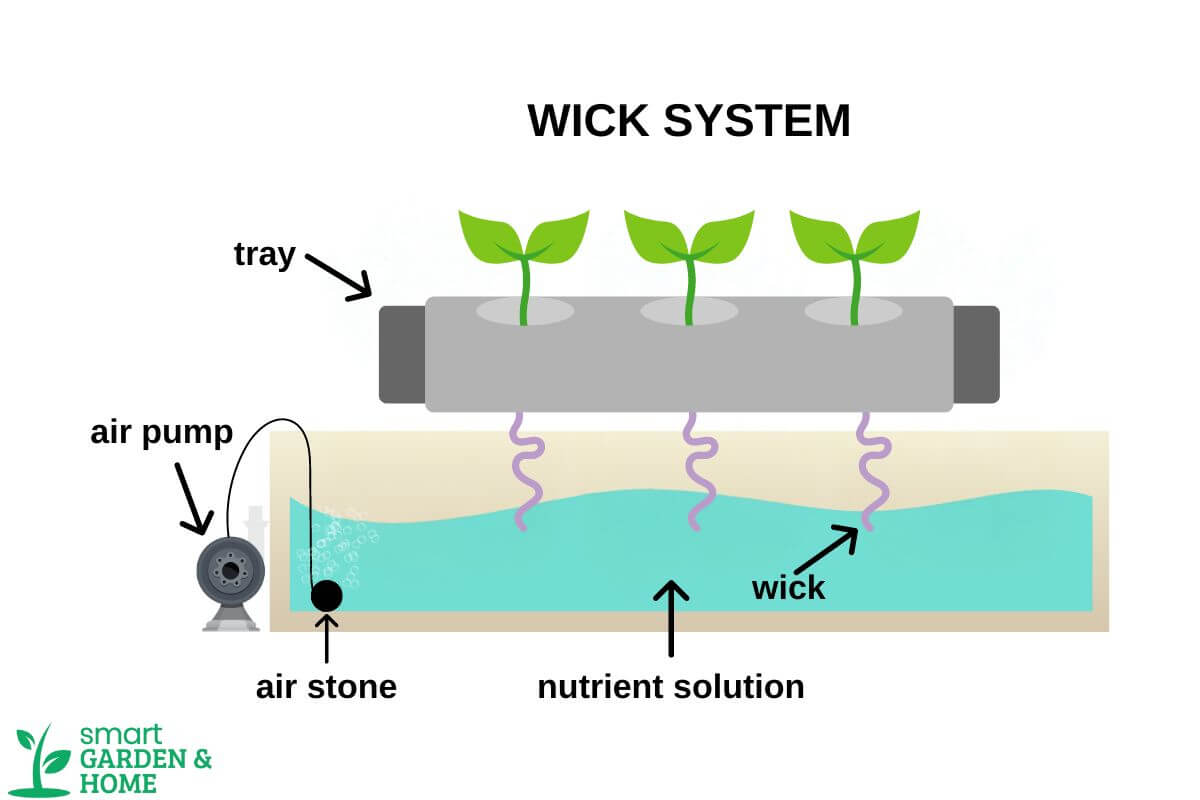
Wick systems are great for beginners as it is the simplest form of hydroponics. This easy-to-use hydroponic system is straightforward and requires no electricity.
Plants are placed in an absorbent growing medium such as vermiculite, perlite, polystyrene packing peanuts, or wood fiber on a grow tray.
Wicks run from the plant roots down into a nutrient solution reservoir. The wicks then deliver this nutrient water to the plant roots. This passive hydroponics system lets you grow plants without much effort or monitoring.
Wick systems are best for small herbs, flowers, and plants that don’t need many nutrients. Starting with a wick system is a great way to test it out if you’re unsure about hydroponics.
2. Drip System – A Flexible System

Drip hydroponics are easy to set up but require electricity and a small water pump. A water reservoir filled with nutrient-rich liquid fertilizer is placed below the drip tray where your plants are.
The water pump moves the nutrient water from the reservoir up to the drip tray. This water feeds the plants, and any extra water drips back down into the reservoir, starting the cycle again.
This system is very flexible. You can make it as large or small as you need to grow your favorite plants, fruits, and vegetables.
3. Deep Water Culture System – Best for Growing Fruits and Vegetables

Water culture systems or Deep Water Culture (DWC) systems keep the entire plant root system submerged in nutrient-rich water in a storage area, often called a bubble bucket. The bubble bucket is then filled with nutrient-rich liquid, and the plants are gently placed in this solution.
Perforated cups, also known as net cups or net pots, hold the roots to keep them from sinking completely. This allows the leafy parts of the plants to stay above the water, capture light, and go through photosynthesis.
An air pump can be added to oxygenate the water, which can greatly boost your plant’s growth rate.
A constant stream of fresh water made available to the roots can help you grow your favorite fruits and vegetables much faster than traditional methods.
- Learn more about Deep Water Culture (DWC) Systems
4. Ebb and Flow Systems – Great for Home Gardeners
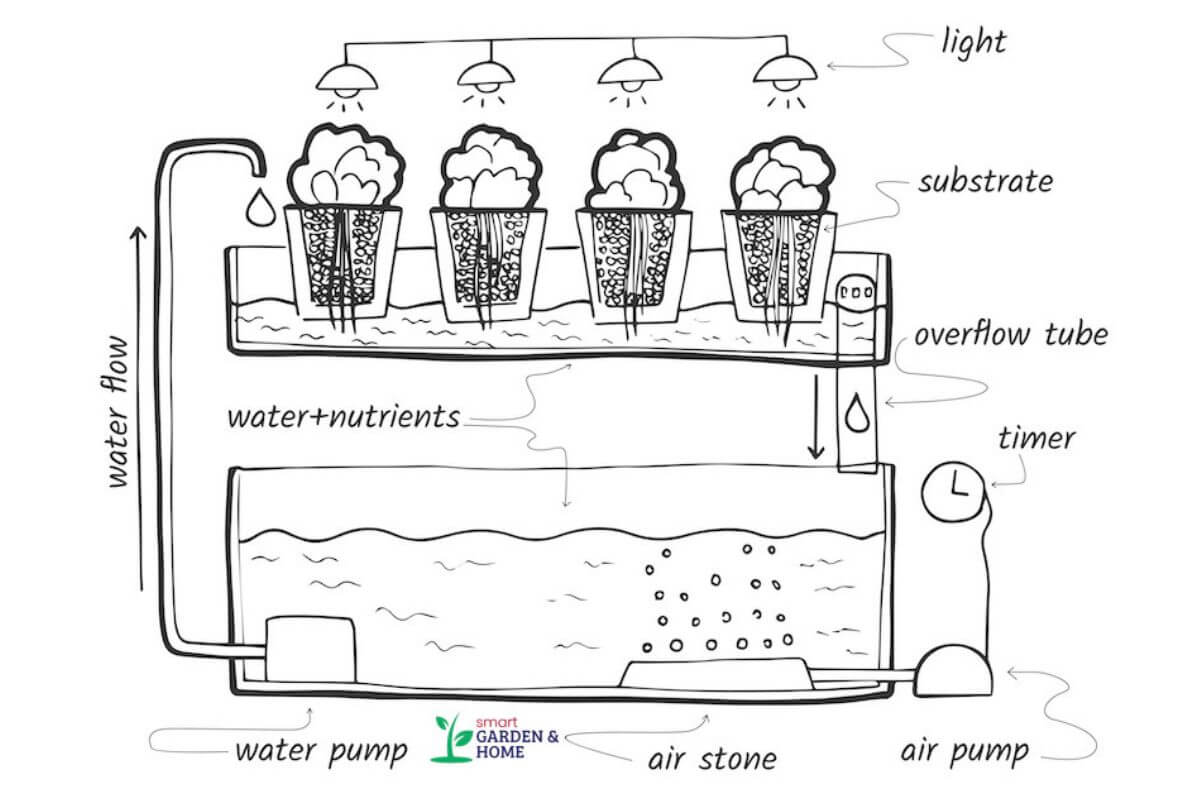
Ebb and flow hydroponics or flood and drain systems are loved by home gardeners. This system periodically floods the grow bed with nutrient solution and then drains it back.
This cycle ensures roots get both nutrients and oxygen, important for optimal plant growth. Go for this system if you want to mimic natural tidal systems that plants love.
- Learn more about Ebb and Flow Systems
Plants are placed in grow beds filled with a medium in hydroponics, like rock wool. The bed sits on a grow tray that is flooded with nutrient-rich water by a water pump.
- Discover more about the Different Hydroponic Growing Mediums
The pump stops and the water drains back into the reservoir after the water reaches a certain height determined by the overflow tube. Automatic timers control the pump, flooding the tray again until the water reaches the overflow tube, then draining it back down.
This ebb-and-flow cycle repeats, boosting oxygenation, nutrient retention, and plant growth.
5. Nutrient Film Technique System (NFT) – Ideal for Smaller Plants
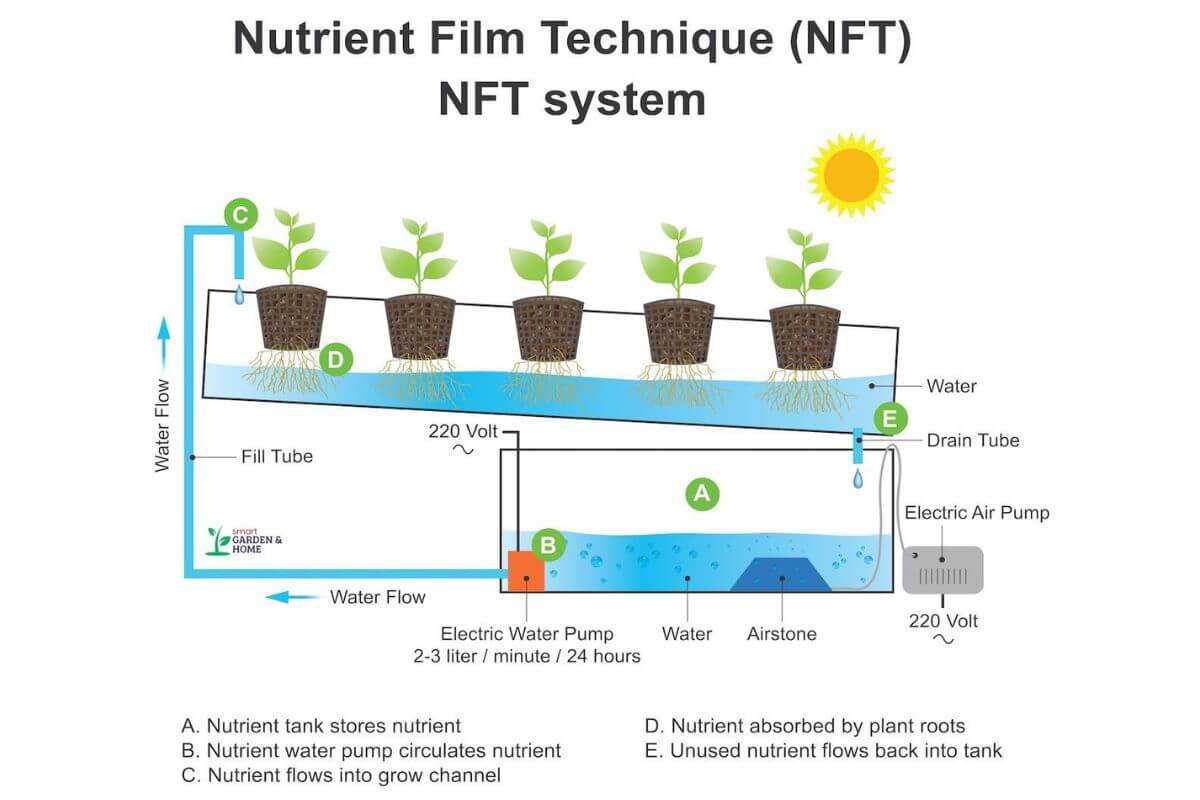
Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) systems are ideal for growing smaller plants, herbs, and leafy greens. It works by placing plants on sloped trays. Nutrient-rich water is then pumped from a holding tank to the top of the sloped tray.
The water flows down the slope, washing over the plant roots with nutrients, then drains back into the reservoir to be pumped up again. These systems are very scalable. You can find easy-to-follow blueprints and plans to build an NFT system yourself.
NFT systems can be customized to fit the size you need, ensuring efficient use of resources and optimal plant growth.
- Read more about the Nutrient Film Technique (NFT)
6. Aeroponics System – Prevents Plant Drowning and Ensures Watering Efficiency
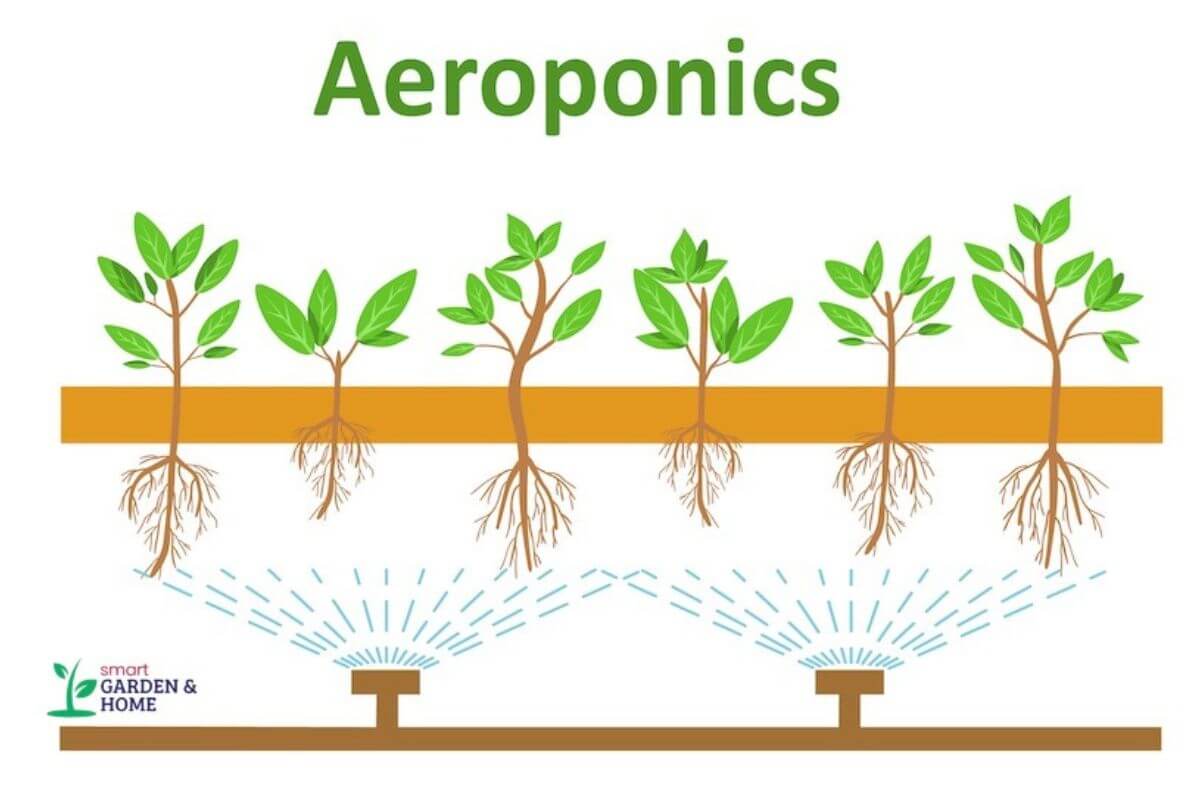
Aeroponics systems are a more challenging method of crop production, even though the concept is simple.
Plants are suspended in the air in an aeroponics system, and their roots are regularly misted with nutrient-rich water from spray nozzles. The leafy parts of the plants are protected from the spray with a cover that separates the top and bottom portions.
Aeroponic systems are great because the plant’s roots aren’t submerged in water, preventing drowning, and water is efficiently reused.
However, these systems can be tough for beginners to build and maintain, which is a downside.
- Learn more: What Is Aeroponics?
7. Kratky Method of Hydroponics – For Passive Beginners
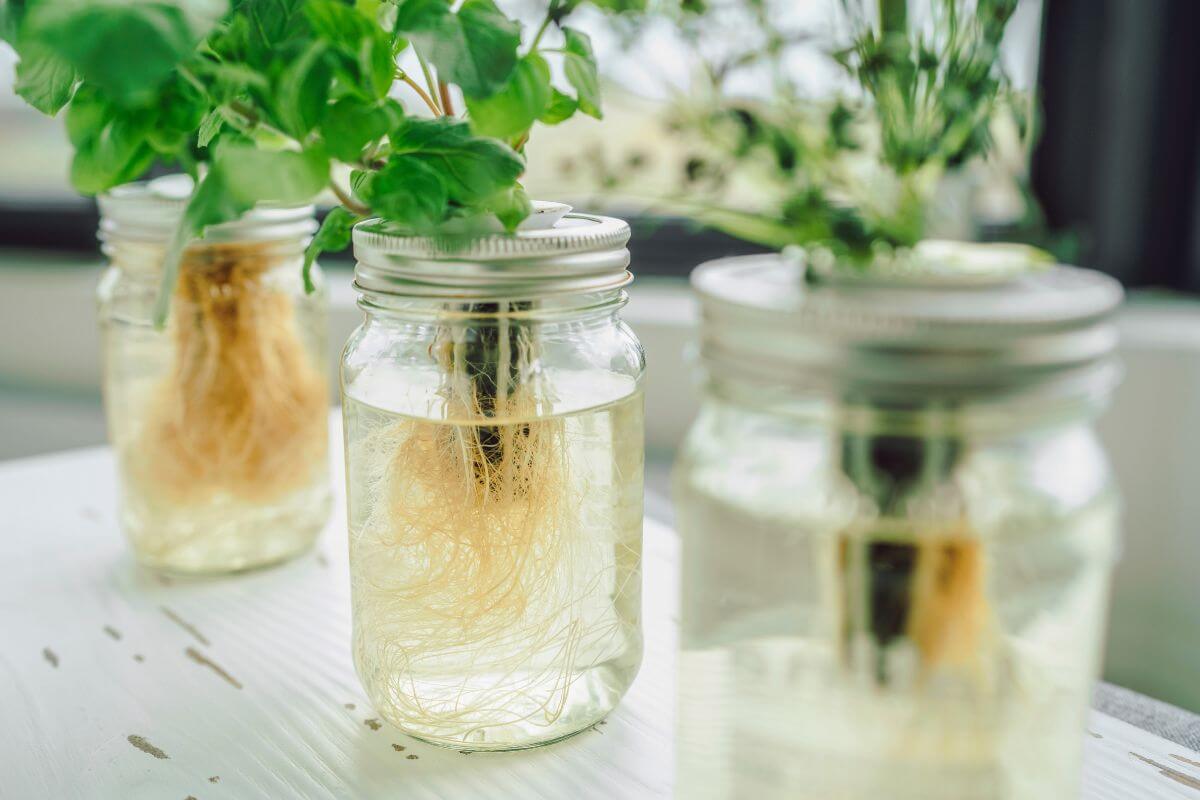

The Kratky Hydroponics Method is a straightforward and passive system named after its creator, Dr. Bernard Kratky from the University of Hawaii (source). This method is perfect for beginners who want to go into hydroponic gardening since you don’t need expensive equipment or constant monitoring.
What’s great about Kratky hydroponics is its simplicity. It doesn’t require electricity or pumps to circulate nutrients, making it cost-effective and low-maintenance for small-scale gardening.
Plants are placed in net cups in this set-up. The cups are filled with a medium capable of capillary action like rock wool, expanded clay aggregate, sphagnum moss, or coconut coir.
These cups hang above a water reservoir containing essential nutrients in solution. Only the tips of the roots touch the water’s surface.
A moist air gap forms between the water and the plant base as the plant grows and the water level decreases. Roots in this space develop into lateral “oxygen roots,” absorbing oxygen from the air within the container.
The plant is usually ready for harvest by the time the water level is depleted. This means no additional water or nutrients need to be added throughout the growing cycle beyond the initial setup.
The Kratky method works best when growing leafy greens, herbs, and smaller plants. However, it’s not suitable for plants with high water needs or long growing times.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Hydroponics?

Hydroponics offers a fascinating way to grow plants without soil, but it has its upsides and downsides like any method. Let’s take a closer look at some advantages and disadvantages of hydroponic gardening.
Advantages of Hydroponics
Hydroponic gardening brings several advantages to the table. Let’s explore how this innovative method can transform the way we grow plants.
- Accelerated Growth – Hydroponic plants grow 20% to 30% faster than those in traditional gardens, thanks to nutrient-rich mediums that outperform soil fertilizers.
- Water Efficiency – Hydroponics uses less than 10% of the water consumed by traditional farms, contributing to water conservation and sustainability efforts.
- Soil-Free Crop Production – Indoor vertical farming in hydroponics is not affected by either climate or soil quality. This marks a significant shift in agriculture, offering versatility and resilience.
- Environmental Control – The wide variety of hydroponic systems provides complete control over a growing environment. This ensures optimal conditions for consistent and superior results.
- Reduced Pesticide Use – Hydroponic farms minimize the need for pesticides for plants grown in protected environments, promoting food safety.
- Efficient Troubleshooting – Hydroponic farming simplifies problem-solving by offering clear insights into growth issues. It facilitates quicker resolutions and improves system management.
- Sustainable Farming – Hydroponics offers a green solution to farming by mitigating soil degradation and water waste. This reduces carbon footprint, and supports eco-friendly practices, like no longer need for crop rotation.
- Hyper-Local Food Systems – Hydroponics enables the creation of hyper-local food systems, where produce is harvested and served immediately. This improves freshness and the Farm-to-Table dining experience.
Disadvantages of Hydroponics
While hydroponic gardening offers numerous advantages, it also comes with its own set of challenges. Here’s a breakdown of the downsides to consider before trying this method of plant cultivation.
- Initial Investment Costs – Setting up a hydroponic system can be costly, as you’ll need various equipment like pumps, lights, filters, fans, containers, and growing mediums.
- Active Management Required – Hydroponics is not a hands-off approach to farming. It would require some level of attention even with its passive options. You still need to stay on top of monitoring and adjusting systems to ensure optimal conditions for plant growth.
- Vulnerability to Power Outages – Most hydroponic setups rely on electricity to function. Whether due to a storm or a blackout, a single power failure can put the health of your plants at risk by disrupting nutrient delivery. It’s essential to have contingency plans in place to mitigate risk.
What Is Hydroponics Final Thoughts
With a rising interest in organic food production, technology has made hydroponic systems more accessible than ever. We’re also armed with more knowledge than before so the options and opportunities to work on these ideas about hydroponics are bigger.
There may be some learning curves for beginners, but fear not! There are several options that you can try, particularly the wick system. It may take time, but you should eventually find what works for you.
As urban areas grow, so does the demand for locally sourced produce. While it’s not proven that plants grown hydroponically are healthier, hydroponics still offers a sustainable farming solution for the future.
It is an alternative to traditional farming that reduces transportation costs and ensures consistent supply year-round, regardless of weather conditions.
What Is Hydroponics FAQs
1. Why Is It Called Hydroponics?
In hydroponic gardening, the term “hydro” comes from the Greek word for water, and ‘”ponos” means work. So, hydroponics means “water working”. Instead of soil, water takes on the task of delivering nutrients directly to the plant roots.
2. What Type of Light Do I Need for Indoor Hydroponics?
For indoor hydroponics, you have options like high-intensity discharge (HID), fluorescent lights, and light-emitting diodes (LED lights). When picking a lighting option, it would help to think about both cost and energy efficiency.
3. How Much Space Do I Need to Set up an NFT System?
The size of your hydroponic system depends on how much indoor space you have and the demand for the crops you want to grow. For example, a table-top NFT system usually has six 4-foot-long channels and measures about 55 inches by 55 inches by 31 inches (length, width, height). With this size, you can accommodate up to 36 plants per table.
If you’re interested in learning more about hydroponic systems, check out these articles:

